Dioxines
Laboratoire des dioxines
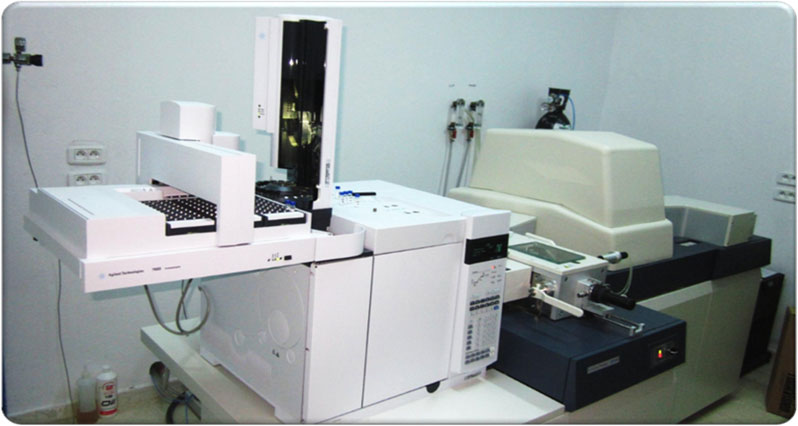
Chromatographe en phase gazeuse haute résolution couplé à un spectromètre de masse haute résolution (GCHRMS)



Tunisian republic
Ministry of Industry, Mines and Energy
Central Laboratory for Analysis and Testing
Chromatographe en phase gazeuse haute résolution couplé à un spectromètre de masse haute résolution (GCHRMS)

Veterinary drugs are used in farms for the health and growth of animals: cattle, poultry, fish, shrimp, bees, etc .
Antibiotic residues can be found in foodstuffs (meat, fish, milk, eggs and honey) obtained from these treated animals as a result of faulty practices such as non-compliance with the expectation or abuse of growth promoters.
Due to the potentially carcinogenic and toxic properties of antibiotic residues and their allergic potential, maximum residue limits (MRLs) have been set for pharmacologically active substances (Regulation (EU) No 37/2010 and its successive amendments) .
In the final food product, the molecule is either prohibited with zero tolerance or permitted up to a defined level, depending on its nature and destination.


Residues of veterinary medicinal products detected:

Radioactive contamination is the phenomenon that occurs when a radioactive product is deposited on an object or a being, or is ingested or inhaled by a being. Contamination can spread in the food chain (human and animal), than in others (pharmaceutical, industrial, etc.).
In the aftermath of the Chernobyl accident (1986), the national authorities responsible for technical import control took the decision to subject all imported food products to systematic control of the level of radioactive contamination. The LCAE has since been equipped with a NaI scintillation Gamma detector allowing the measurement of Cesium 137 and 134 contamination. New equipment has been added to the analytical park and now allows the measurement of two other radioactive elements (Cobalt 60 and Iodine 131) .


Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are chemical contaminants whose formation results from the incomplete combustion of organic products. These molecules are toxic to humans: some PAHs are carcinogenic and genotoxic.
The contamination of foodstuffs by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can be of environmental origin (emission into the environment or pollution such as oil spills) but the major source of contamination of foodstuffs by PAHs is linked to treatment processes. heat of food (for example, cooking by grilling, smoking, etc.).
Benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P) (used as a marker of food contamination by PAHs) and the sum of four specific substances (HAP4) are regulated in certain categories of foodstuffs by the decree of 13 May 2013 and Regulation (EU) No. 835/2011 amending Regulation (EC) No. 1881/2006




| Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites with a toxic action on humans and animals. They are synthesized by fungi of the mold type (Aspergillus sp., Fusarium sp, etc.) in the fields or in the storage of foodstuffs. Cereals are the most affected, but fruits can also contain mycotoxins. Their presence in products intended for human consumption and animal feed can have an adverse impact on health such as carcinogenic and mutagenic effects and can also cause estrogenic, gastrointestinal and renal disorders. |
The mycotoxins laboratory is thus able to search for and quantify the mycotoxins covered by the decree of May 13, 2013 setting the list of maximum limits for certain contaminants in foodstuffs and the methods for taking samples and analysis for official control and European regulations (EU 1881/2006, EU 401/2006 and EU 2002/32).


The field of activity covers a wide variety of matrices intended for human and animal consumption:



The laboratory detects and quantifies many mycotoxins:
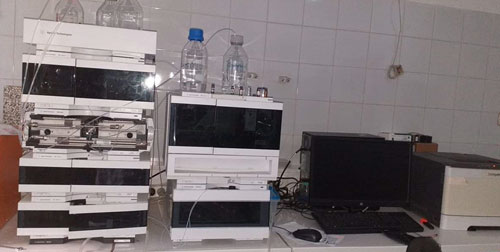
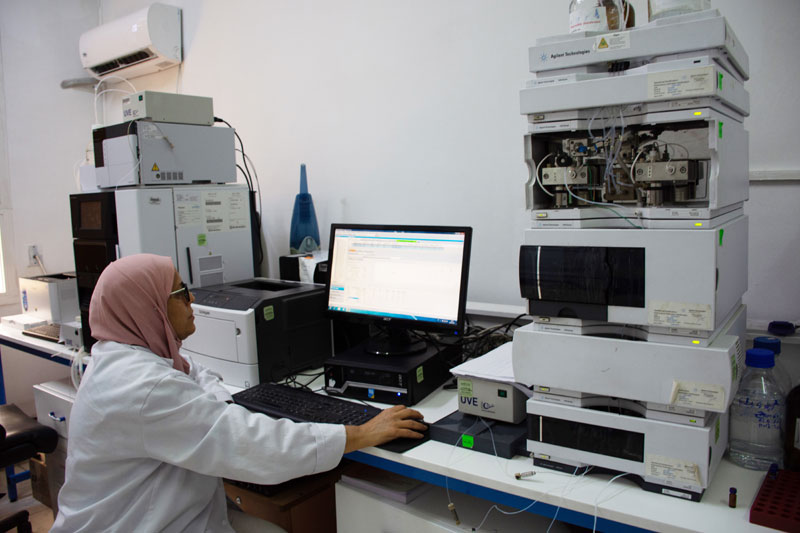
The laboratory is equipped with two HPLC-Fluorescence chromatographs which makes it possible to reach the limits required by the regulations